Chicago Auto Accident Lawyer
Truck Driving Laws and Regulations
Truck driving laws and regulations are crucial for preventing dangerous accidents along Chicago’s largest routes, such as the Kennedy Expressway or the Jane Byrne Interchange. A Chicago truck accident attorney from our firm will investigate your crash and determine whether violations of state or federal regulations contributed to the crash. Contact us today for a free consultation

What Are the Primary State and Federal Regulations Governing Trucking in Chicago?
Truck drivers and trucking companies must comply with both state and federal regulations. The first of these is the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), which oversees the trucking industry at the national level.
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) sets minimum standards for interstate commerce. However, the FMCSA requires trucking companies to comply with federal guidelines when state laws are less restrictive (49 U.S. Code § 31141).
Illinois generally aligns its laws with federal regulations, but in some cases, it is more restrictive. In these instances, commercial vehicle drivers must comply with Illinois law.
FMCSA Regulations
Federal trucking regulations apply to most commercial motor vehicles engaged in interstate commerce. This includes commercial truck drivers and trucking companies that operate on federal or interstate highways.
Violations of federal trucking regulations, particularly those around driving time and weight regulations, can establish negligence in truck accident cases.
Illinois Trucking Laws
Illinois highways are managed by the Illinois Department of Transportation (IDOT), which collaborates with federal agencies to prevent accidents. IDOT enforces state regulations, investigates truck crashes, and ensures public safety through collaboration with the Illinois State Highway Patrol.
While Illinois trucking laws and regulations typically align with federal law, the state has additional requirements for weight limits, weight restrictions, and vehicle maintenance. Additionally, Illinois issues overweight permits and sets limits on transporting hazardous materials along certain roadways.
What Are Key Trucking Regulations?
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) is the primary source of truck safety resources. These regulations help to prevent driver fatigue, ensure safety through inspections and weight regulations, and prevent accidents through drug testing.
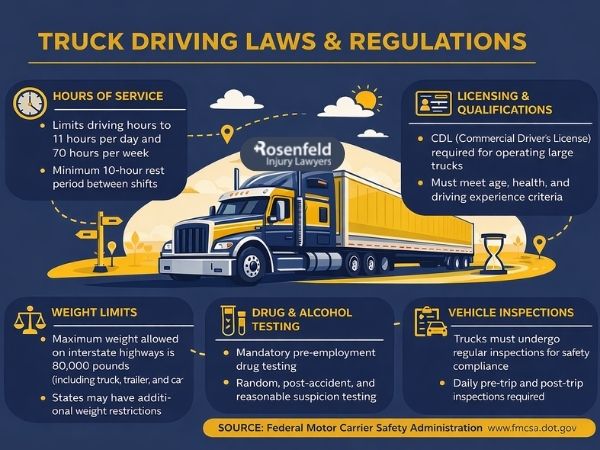
Truck Drivers’ Hours of Service Regulations
Hours-of-service regulations (49 CFR Part 395) are a critical safety measure, ensuring that commercial truck drivers are not sleep-deprived. There are different HOS regulations depending on whether drivers are transporting passengers or cargo.
The FMCSA regulations for drivers carrying cargo along interstate highways are as follows:
- 11 hours of service after 10 consecutive hours off duty
- Cannot drive after 14 hours of service, even after rest periods
- 30-minute break after 8 hours
- 60/70 weekly limits, depending on a 7-day or 8-day period
- Must have spent at least 10 hours in a sleeper berth
There are hours-of-service exemptions if the truck driver is within 150 air miles of their work location (49 CFR 395.1). Companies must keep truck driver log books proving that drivers are complying with their driving time restrictions.
Trucking Regulations on Vehicle Safety and Maintenance
Poor vehicle maintenance is a common cause of truck accidents, often resulting in catastrophic injuries. Federal regulations require systematic and periodic inspections of brake systems, tires, lights, gears, and tractor-trailer connection systems (49 CFR Part 396).
The Illinois Office of Secretary of State explains what must be checked before every drive in its Illinois CDL pre-trip inspection checklist, available on its website. Additionally, truck drivers must complete a report at the end of each trip highlighting any issues that must be repaired before the next dispatch (49 CFR 396.11).
Federal reflective tape requirements for trucks ensure that vehicles are conspicuous at night, which prevents serious accidents (49 CFR 393.11). At least 50% of the total length of the vehicle must have reflective tape, and the lower rear of the vehicle must be entirely covered.
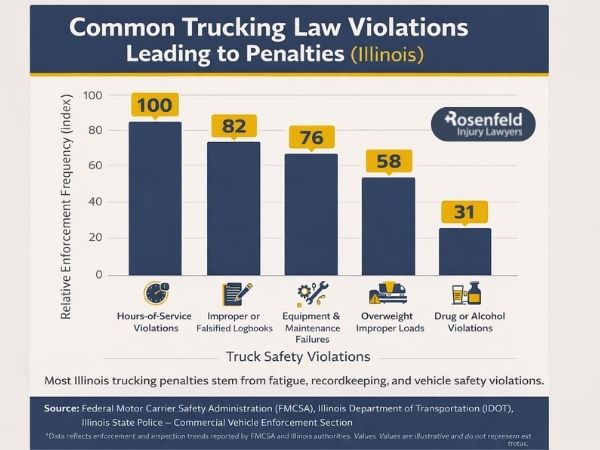
Weight Restrictions and Load Limits for Commercial Trucks
Weight regulations and weight restrictions are essential for keeping both infrastructure and people safe. Large vehicles need a greater stopping distance and are more difficult to control, which can lead to catastrophic injuries in an accident.
Illinois truck weight limits utilize the Federal Bridge Formula, which determines how much weight can be distributed per axle to avoid damaging bridges. In Illinois, the maximum gross vehicle weight rating is 80,000 pounds (625 ILCS 5/15-111). While most commercial vehicles comply with this rule, vehicles that are above 80,000 pounds may be able to apply for an overweight permit from IDOT.
CDL Requirements and Driver Qualification Rules
Truck drivers must have a valid commercial driver’s license (CDL) (49 CFR 391.11). Illinois CDL requirements include:
- At least 18 for intrastate commerce, or 21 for interstate commerce
- Medical certification from a DOT-certified medical examiner
- Passed an FMCSA-approved Entry-Level Driver Training course
- Pass the three-part CDL exam
Motor carriers must maintain a Driver Qualification File for each of their truck drivers (49 CFR Part 391). If they fail to do so, they can be held directly and vicariously liable for a truck crash (McQueen v. Lavonta M. Green).
Drug and Alcohol Testing Under FMCSA Regulations
Illinois follows FMCSA Drug and alcohol testing guidelines, which include:
- Pre-Employment Testing: This covers controlled substances only (49 CFR 382.301(a)).
- Random Testing: Every carrier must test at least 10% of their drivers for alcohol use and 25% of their drivers for controlled substances every calendar year (49 CFR 382.305).
- Reasonable Suspicion: Carriers must request drug and alcohol testing if they believe one of their drivers is using during their driving time (49 CFR 382.307).
- Post-Accident Testing: After a truck crash, all surviving drivers must be tested for both alcohol (49 CFR 382.303(a)) and controlled substances (49 CFR 382.303(b)).
Failure to comply with any testing is considered a positive, and such violations can lead to suspension. A failed or skipped test, or a company’s failure to test, can be powerful evidence for a personal injury claim.
Hazardous Materials and Cargo Securement Rules
Cargo securement rules ensure that loads do not shift or spill during transport, which prevents serious accidents (49 CFR 393.100).
There are strict regulations governing the transportation of hazardous materials, including placards, specialized training, and parking vehicles to prevent leaks (49 CFR Part 397). If truckers carry cargo that could shift or spill, they must ensure it is properly secured and sealed before being dispatched.
How Violations of Trucking Laws Lead to Truck Accidents
Some of the most common causes of truck accidents include distracted driving and fatigue, which is why drivers must comply with all FMCSA and state regulations. Federal restrictions on phone use by commercial drivers are designed to avoid distracted driving behaviors like texting and driving, which are in line with the Illinois Vehicle Code’s restriction on handheld cell phone use (625 ILCS 5/).
Fatigued driving can result from medical issues, even when drivers comply with hours-of-service restrictions. As such, drivers must adhere to DOT sleep apnea requirements regarding CPAP use in order to receive medical certification.
How a Chicago Truck Accident Lawyer Can Help
Our Chicago truck accident lawyers will carefully investigate the accident and identify whether trucking regulation violations played a role in the crash. We will review electronic logging devices, maintenance reports, and driver qualification files, and also consult with trucking industry experts who can provide their unbiased perspective on how the crash occurred.
Next, we will negotiate with the trucking company’s insurance carrier to receive a fair settlement for your injuries. While the minimum liability insurance for trucking companies is $750,000, insurers often limit coverage. An experienced truck crash lawyer can thoroughly evaluate your damages, build a strong case, and negotiate for a settlement that covers all your needs.
Book a Free Case Review
Our Chicago traffic accident lawyers have helped over 5,000 clients over the past 25 years, securing more than $450 million in compensation. With our deep knowledge of trucking industry regulations, our Super Lawyers® can identify violations and demonstrate negligence by drivers, employers, cargo loaders, and maintenance companies. This gives you the best possible chance at receiving a fair settlement.
We work on a contingency fee basis: no fees unless we win. Contact us today for a free consultation about your truck crash claim.







